
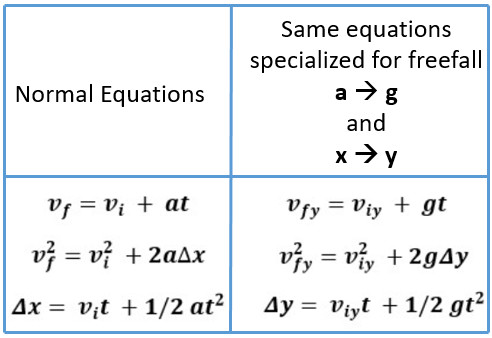
Acceleration due to gravity is constant, which means we can apply the kinematic equations to any falling object where air resistance and friction are negligible. The acceleration of free-falling objects is therefore called acceleration due to gravity. The force of gravity causes objects to fall toward the center of Earth.
PHYSICS FREEFALL EQUATIONS FREE
(It might be difficult to observe the difference if the height is not large.) Air resistance opposes the motion of an object through the air, and friction between objects-such as between clothes and a laundry chute or between a stone and a pool into which it is dropped-also opposes motion between them.įor the ideal situations of these first few chapters, an object falling without air resistance or friction is defined to be in free fall. A tennis ball reaches the ground after a baseball dropped at the same time. In the real world, air resistance can cause a lighter object to fall slower than a heavier object of the same size. Describe how the values of the position, velocity, and acceleration change.

Scott demonstrated in 1971 on the Moon, where the acceleration from gravity is only 1.67 m/s2 and there is no atmosphere. Use the kinematic equations with the variables y and g to analyze free-fall motion. This is a general characteristic of gravity not unique to Earth, as astronaut David R. If a ball is thrown upward, the equations of free fall apply equally to its ascent as well as its descent.įigure 3.26 A hammer and a feather fall with the same constant acceleration if air resistance is negligible. But “falling,” in the context of free fall, does not necessarily imply the body is moving from a greater height to a lesser height. For example, we can estimate the depth of a vertical mine shaft by dropping a rock into it and listening for the rock to hit the bottom. Let’s assume the body is falling in a straight line perpendicular to the surface, so its motion is one-dimensional. vi : is the initial velocity of the object in the ydirection. If the origin is taken at ground level, then: yi : is the initial height of the object at time zero.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
